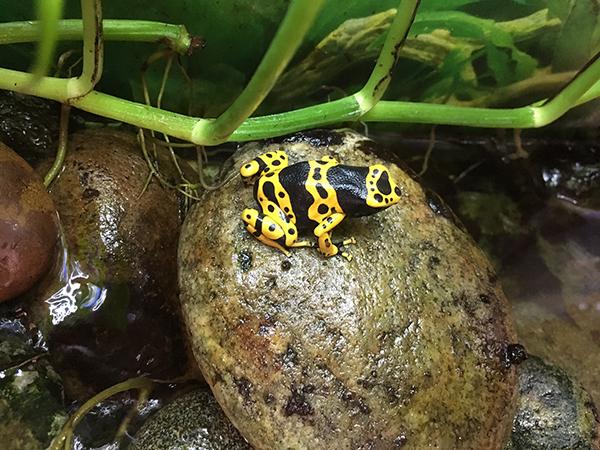
Yellow and Black Poison Frog
Yellow and Black Poison Frog
Dendrobates leucomelas

Printable Care Sheets
Explore More!
General Information
Family: Dendrobatidae
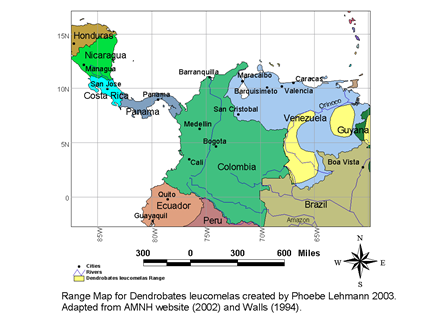
Locale: Brazil; Colombia; Guyana; Venezuela
Habitat: Found in moist or wet forests in lowlands, found in leaf litter on forest floors or occasionally on trees at temperatures of 26° to 30°C.
Average Size: Range from 3.1 to 5 cm (1.2 to 1.97in) with average of 4 cm (1.57in)
Average Lifespan: 10 to 15 years, but the oldest known lived to 20.5 years
Activity: Diurnal
Care Summary
*Note: Be sure to check out the care sheet for Poison Dart Frogs in general as well
Captive care: Rainforest terrarium: a breeding pair or trio can be housed in a 10 gallon well-planted aquarium with good drainage. Expanded clay pellets covered with sphagnum moss and planted with pothos and bromeliads works well. Water should be shallow as these frogs are not strong swimmers and can drown. A small hide, such as half a coconut shell or flowerpot will provide a breeding site. The tank should be covered with a hinged glass lid that has 1.5-2 inches of plastic along back in which ~6 small holes have been drilled (allows air exchange while maintaining high humidity, 95%). A small pump can be used to generate a stream, put pump in one corner (cover with clay pellets) and run aquarium tubing under rock to other corner where rocks are piled to generate a waterfall and rock stream.
Temperature: Poison dart frogs prefer moderate temperatures. Daytime temperatures between 75°F and 84°F (23.5°C to 29°C).
Lighting: Frogs need light to see their food, and full spectrum lighting is needed to maintain the plants.
Diet: Insectivores: in captivity, the frogs are fed flightless fruit flies or pinhead crickets daily. Insects should be dusted with vitamin calcium mix (2-3 parts Herptivite: 1 part RepCal). The frogs are visual eaters, so they will go after the flies when they see them moving. Adult frogs can eat 50 to 75 fruit flies in a day and juveniles can eat 20 to 30 flies.
Breeding: Sexual maturity is reached at about 2 years. Breeding occurs during the wet season, February to March, and females will lay multiple clutches of 2-12 eggs. Fertilization is external. Eggs hatch in 10-14 days and tadpoles metamorphose by 70-90 days. In captivity, the frogs can be heavily misted as well as heavily fed in order to simulate the wet season.
Notes: While captive bred poison frogs are not poisonous, they are very fragile and thus should not be handled. When moving frogs, chase them into small plastic container (e.g., ketchup cup) and put lid on, move to new location, and allow them to climb out of container.
References
Brennan, L. (2005) "Dendrobates leucomelas" (On-line), Animal Diversity Web. Accessed September 19, 2016 at http://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Dendrobates_leucomelas/
Enrique La Marca, Claudia Azevedo-Ramos. (2004) Dendrobates leucomelas. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2004: e.T55191A11255828. Accessed on September 20, 2016 at http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2004.RLTS.T55191A11255828.en.
Lehman, P. (2003) Dendrobates leucomelas. AmphibiaWeb: Information on amphibian biology and conservation. [web application]. 2016. Berkeley, California: AmphibiaWeb. Accessed September 19, 2016 at http://amphibiaweb.org/.http://www.amphibiaweb.org/cgi-bin/amphib_query?where-genus=Dendrobates&where-species=leucomelas
Walls, J. G. (1994) Jewels of the Rainforest: Poison Frogs of the Family Dendrobatidae. J.F.H. Publications, Neptune City, New Jersey.
Photo: Neal Cropper
Range Map: Phoebe Lehmann, 2003. Adapted from AMNH website (2002) and Walls (1994).
Compiled by Eileen Underwood, 9/2016.
Related Projects
by students in the BGSU Herpetarium
The Herpetarium is a facility in the Department of Biological Sciences.
Bowling Green State University | Bowling Green, OH 43403-0001 | Contact BGSU Herpetarium | Campus Map
Updated: 04/13/2021 12:22PM


